تعريف تتفاعل به: RFID (مذياع تحديد التردد), المعروف باسم “العلامة الإلكترونية”, هو تقنية تحديد الهوية التلقائية بدون الاتصال التي تتعرف تلقائيًا الهدف ويحصل على البيانات ذات الصلة من خلال إشارات التردد اللاسلكي. ال لا تتطلب أعمال التعريف التدخل اليدوي كإصدار لاسلكي من الباركود. تكنولوجيا RFID لديها مزايا للماء, مكافحة المغناطيسي, مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية, الخدمة الطويلة في الحياة, وبعد القراءة الكبرى, تشفير البيانات على الملصق, سعة تخزين البيانات بشكل اكبر, وتخزين مجاني معلومة. سوف يكون التطبيق لتجارة التجزئة, الخدمات اللوجستية والصناعات الأخرى أحدثت تغييرات ثورية.
التكوين الأساسي للRFID
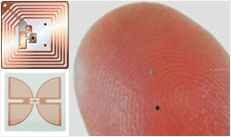
تتكون علامة RFID فعليًا من ثلاثة أجزاء: علامة, هوائي, وقارئ.
بطاقة: يتكون من عنصر اقتران و رقاقة. كل علامة ورمز الكتروني فريد من نوعه. العلامة الإلكترونية عالية السعة يحتوي على منطقة كتابة مستخدم مرفقة بالكائن لتحديد الكائن الهدف.

قارئ: والجهاز الذي يقرأ (و يكتب في بعض الأحيان) علامة المعلومات، ويمكن أن تكون مصممة لتكون يده أو ثابتة;
هوائي: ينقل إشارات التردد اللاسلكي بين العلامة والقارئ.
ميزات RFID
مخزن البيانات: مقارنة بالتقليدية أشكال العلامات, قدرة أكبر (1 قليلا – 1024 قليلا), يمكن تحديث البيانات في أي وقت, ويمكن قراءة وكتابة;
سرعة القراءة والكتابة: مقارنة مع الرمز الشريطي, أنها لا تحتاج الخطي مسح محاذاة, والقراءة و سرعة الكتابة أسرع, والتي يمكنها التعرف على الأهداف المتعددة والحركة التعرف على;
سهل الاستخدام: مقاس صغير, سهلة ل صفقة, يمكن أن تكون جزءا لا يتجزأ في المنتج;
الأمان: الشريحة المخصصة والمسلسل الرقم فريد ويصعب نسخه;
متين: لا عطل ميكانيكي, طويل الحياة ومقاومة البيئات القاسية.
كيف يعمل تتفاعل
مبدأ العمل الأساسي لـ RFID التكنولوجيا ليست معقدة: ينقل القارئ ترددًا محددًا لـ إشارة تردد الراديو من خلال هوائي الإرسال, ويولد ملف مستحث عند دخول العلامة الإلكترونية إلى منطقة العمل الفعالة, وبالتالي الحصول على الطاقة, ويتم تنشيط العلامة الإلكترونية, بحيث أن العلامة الإلكترونية تشفر نفسها. يتم إرسال المعلومات من خلال المدمج في هوائي RF; هوائي استقبال القارئ يستقبل الإشارة المعدلة مرسلة من العلامة, وينقلها إلى وحدة معالجة إشارة القارئ عبر الضابط الهوائي. بعد الإستخلاص وفك, المعلومات الصحيحة هي يتم إرسالها إلى نظام مضيف الخلفية. معالجة المترابطة; النظام المضيف يحدد هوية العلامة وفقًا للعملية المنطقية, و يؤدي المعالجة والتحكم المقابلة لإعدادات مختلفة, و أخيرًا يصدر إشارة أوامر للتحكم في القارئ لإكمال عمليات القراءة والكتابة المقابلة.
تصنيف RFID
حسب وجود أو عدم وجود قوة, وهي مقسمة الى السلبية والإيجابية:
علامة سلبية:
المستشعر السلبي نفسه ليس لديه قوة إمداد. التيار الكهربائي هو من قارئ. يرسل القارئ ترددًا إلى جعل المستشعر يولد طاقة ويعيد البيانات إلى القارئ. الحجم خفيف نسبيًا وقصير, ولها الخدمة الطويلة في الحياة. الاستشعار المسافة قصيرة.
العلامة نشطة (نشيط): والثمن هو أعلى. ويرجع ذلك إلى بطارية مدمجة, حجم أكبر من علامة سلبية, وها لها عمر خدمة طويل ومسافة طويلة للاستشعار.
وفقا لتردد, يمكن أن يكون تقريبًا إلى ثلاث فئات: LF, HF وUF:
تردد منخفض: 100~ 500 كيلو هرتز التردد المنخفض مسافة الاستشعار قصيرة وسرعة القراءة بطيئة. هو أساسا 125 كيلو هرتز ولديه قدرة اختراق جيدة.
تردد عالي: 10~ 15 ميجا هرتز الاستشعار مسافة التردد العالي أطول قليلاً, وسرعة القراءة أيضا أسرع من التردد, الذي هو أساسا 13.56MHZ;
الترا عالية التردد / ميكروويف: ما بين 850 و 950 ميغاهيرتز (UHF) و 2.45 غيغاهرتز, والاستشعار عن بعد هي الأطول, ال السرعة هي الأسرع, واختراق ضعيف.
تطبيق RFID
باعتبارها الناقل البيانات, يمكن للعلامات الإلكترونية تلعب دور تحديد الهوية, تتبع البند وجمع المعلومات. وتشمل التطبيقات:
المنتج مكافحة التزييف ومكافحة العث; إدارة الأشياء الثمينة; التحكم في الوصول / تحديد; المادة / تتبع المنتجات; تأجير الموظفين; النقل والتوزيع; تتبع الأمتعة الهواء; التتبع الالكتروني, التتبع الغذاء; إدارة خط الإنتاج; شبكة السكك الحديدية لإدارة النقل; إدارة المخازن الذكية; الملابس إدارة التصدير متجر بيع بالتجزئة; إدارة مكافحة سرقة, إدارة الاستخدام غير المصرح به أو إدارة الأصول معدات ثمينة; مركبة, موقف للسيارات ومحطة وقود, إدارة مستودع; جمع التلقائي للرسوم الجسر; مهم, مناسبات خطرة إدارة مراقبة الدخول; المؤتمر وتوقيت–تطبيقات نموذجية; إدارة الحيوانات, التغذية شخصية; التعرف الآلي للآلات المكنية CNC; كمية المنتجات ومراقبة عملية في نظم معالجة مرنة; مراقبة المشتبه بهم; نظام الصواريخ المضادة للسرقة وسيارة نظام الإشعال; مكتبة ذكية, إدارة المنتجات الإيجار; تطبيق سرقة السيارات وبدون مفتاح نظام فتح الباب; إدارة التطبيقات من سيارة للحماية من السرقة وبدون مفتاح نظام فتح الباب; تطبيق RFID في إدارة المستودعات; RFID في الكحول لمكافحة التزييف وتطبيق لمكافحة العث; RFID في موقف للسيارات التطبيقات; RFID في تطبيقات إدارة الحيوانات الأليفة; RFID في مجال الخدمات اللوجستية والتطبيقات التوزيع; RFID في المستودعات سأعتمد; يجب أن يكون الحيوان RFID ارجاعها; تطبيقات تتفاعل في إنتاج خط التحكم الآلي





